Find Out If You Have a Food Intolerance
Hassle-free home blood test kits for food intolerance, sensitivity, allergy and health insights. Get informed. Be proactive. Feel better.
SALE: 30% OFF SELECTED TESTS
+ FREE DELIVERY
- 0 Days :
- 0 Hours :
- 0 Minutes :
- 0 Seconds
The UK’s #1
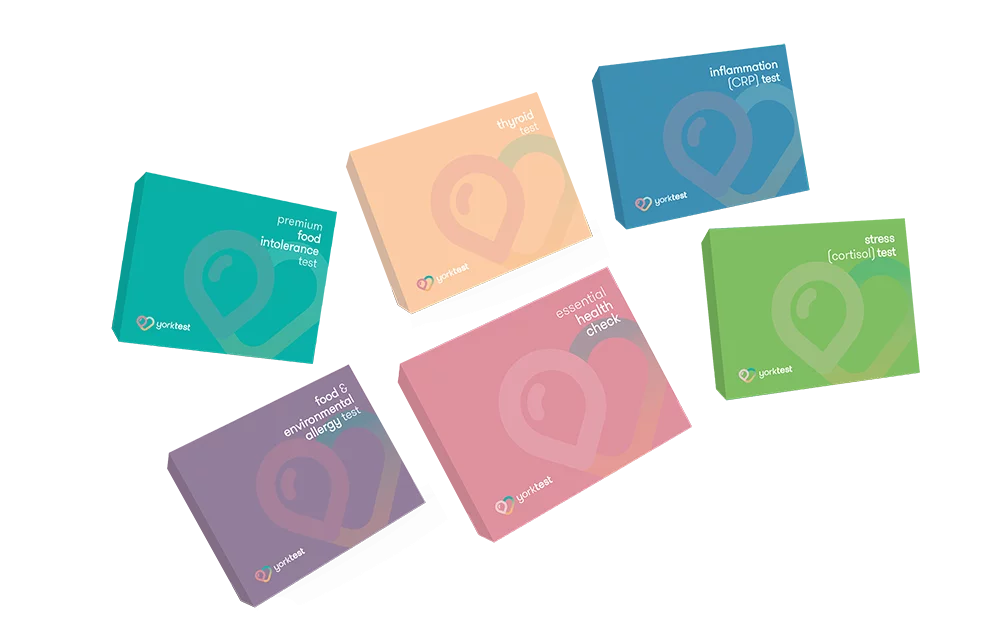
Food Intolerance & Allergy Blood Test Kits
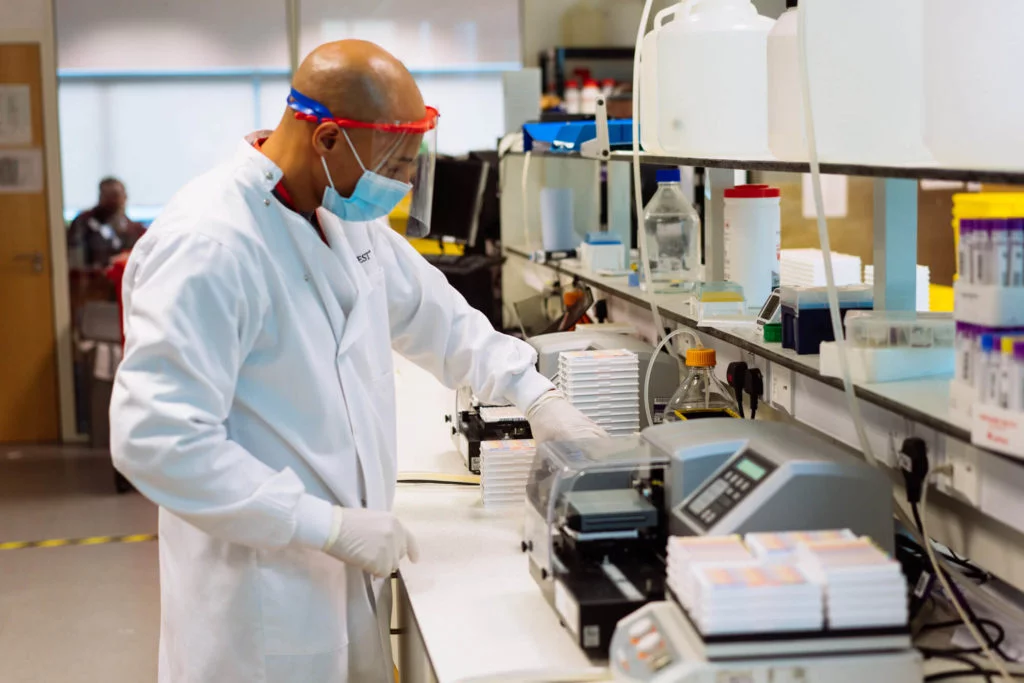
With 40 years’ experience in food intolerance* and food allergy testing, and as a leading home health test provider, we work with you to optimise your diet and help take control of your health and wellbeing.
Why YorkTest?
Many people can go their entire life suffering from symptoms related to IBS, bloating, tiredness and more without even considering a food intolerance*, food allergy test or other health test. Our food intolerance tests have helped thousands of people, to identify their food sensitivities and optimise their diet and health. We’ll do the same for you.

Best Selling Products

Tests For 23 Food Allergies And 19 Environmental Allergens With Our Home Allergy Test
Allergies can be life-changing, with various symptoms like itching, swelling, vomiting, and diarrhoea; we provide food allergy testing to help you to understand what might be contributing and help you take control of your health.
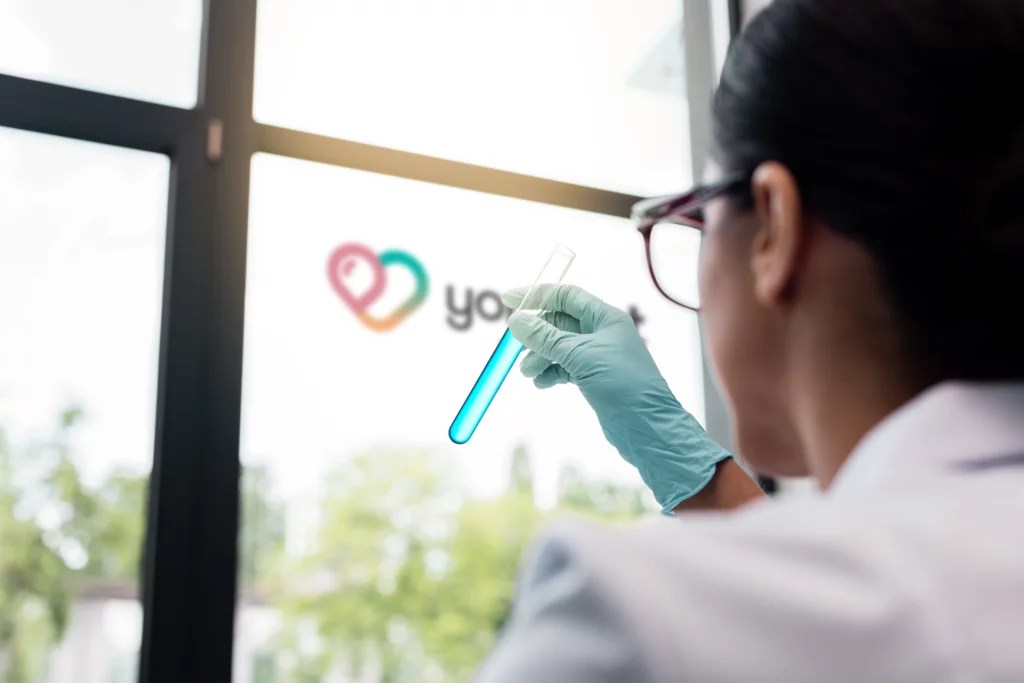
Simply take a quick finger-prick blood sample and return it to our laboratory in the post. You’ll receive your results within 7 days. Some of the environmental and food allergens we test against include: milk, wheat, rice, nuts, chicken, beef pork, cat, horse and dog dander, birch and house dust mites to name a few.
4 Simple Steps To A Better You
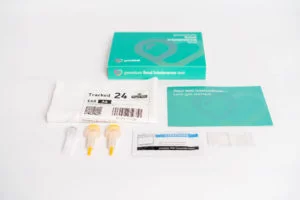
You will receive your testing kit in the post

Take a blood sample with our easy to use finger-prick test kit

Send your sample back in the prepaid envelope provided
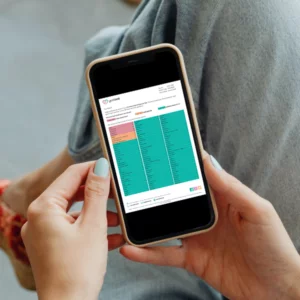
Receive your test results online within 7 days
Nutritional Consultations
When you receive your food intolerance test results, it may be daunting to know what to do next. Our food intolerance test comes with a free 30-minute consultation with one of our Nutritional Therapists. Within this consultation, we will advise you on what foods to eliminate from your diet, and help you find great alternatives so you can still enjoy mealtimes without experiencing the symptoms that come with a food intolerance or food allergy. All of our consultations are bespoke; we can align recommendations regarding your food sensitivities with pre-existing diets (e.g. vegetarian, vegan), and we can also help recommend supplements to heal the gut from the effects of your intolerance.
*Free Nutritional Therapist consultation only available with any Food Intolerance Test purchased

Types of Tests

40 years
experience
40 years experience

Simple home
health testing
Simple home health testing

Nutritional therapist
support
Nutritional therapist support

Quality assured and
accurate results
Quality assured and accurate results
What Makes Us Different?
We have our own ISO13485 audited and certified manufacturing and testing laboratory which places us at the forefront of scientific innovation. We particularly specialise in food intolerance* and food allergy testing to give you a food reactivity profile. Our food intolerance* and food allergy blood testing analyses your blood to identify what items you have a reaction to.
Our food intolerance tests always include a 30-minute nutritional therapist consultation and with all tests we provide ongoing support from our expert in-house customer care team.











